SCR촉매의 NOx 저감성능 데이터베이스 구축을 위한 NOx 배출 특성 연구
Copyright Ⓒ 2020 KSAE / 180-02
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
Various types of research are being carried out in order to reduce the harmful gases of diesel engines, which have advantages of superior output and fuel economy but with more generation of harmful gases compared to LPG, CNG, and gasoline engines. These studies are being conducted worldwide and the regulation on exhaust gas has become stricter in developed countries, such as the US and Europe. Among the various elements of exhaust gas, the reduction of NOx and PM directly affecting the environment and humans is the most critical. The representing technology to reduce PM and NOx is DPF and SCR, respectively. Among the various types of SCR system, NH3/Urea-SCR is the most preferred technology due to the high efficiency of NOx conversion. In this study, NOx conversion efficiency, in accordance with catalyst temperature, space velocity, and NO/NOx ratio, was measured in order to systematize the SCR catalyst NOx reduction performance database. NOx conversion efficiency according to SCR catalyst aging was also measured and analyzed. As a result of the measurement of the NOx reduction efficiency of the SCR catalyst, the reduction efficiency improves as the temperature rises. Reduction efficiency shows a slight decrease when the temperature exceeds 500 °C. It is understood that the net amount of NH3 that can react with NOx decreases because the oxidation rate of NH3 increases at an elevated temperature.
Keywords:
SCR, Catalyst, Urea, NOx, NH3키워드:
선택적 환원 촉매, 촉매, 요소수, 질소산화물, 암모니아1. 서 론
디젤엔진은 다른 LPG, CNG, 가솔린연료 엔진에 비해 우수한 출력과 연비에도 유해 가스를 배출한다는 단점으로 많은 유해가스를 줄이고자 하는 연구가 진행되고 있다. 이러한 연구는 전 세계적으로 이루어지고 있으며 배출가스 규제 범위도 미국, 유럽 등의 선진국으로부터 단계적으로 강화되고 있다.1)
특히 배출가스의 성분 중 환경과 인체에 직접적인 영향을 끼치고 있는 NOx(질소산화물), PM(입자상물질)의 저감이 가장 관건이며 PM은 DPF(Diesel Particulate Filter), NOx는 SCR(Selective Catalytic Reduction) 을 적용하는 것이 대표적인 기술에 속한다.
SCR은 높은 NOx변환효율을 가지는 NH3/Urea-SCR을 선호하는 추세며, 이는 연료의 연소과정에서 발생하는 NH3/urea를 이용한 SCR 촉매는 담체에 담지된 성분에 따라 백금(Pt, 약 175~250 °C), 바나듐(Vanadium, 약 250~450 °C), 그리고 제올라이트(Zeolite, 약 350~600 °C) 계열촉매로 분류할 수 있으며, 이들은 각기 다른 활성온도 창(Operating temperature window)을 가진다.2)
Winkler 등3)은 공간속도, O2의 농도, H2O의 농도, 그리고 NO/NO2 비에 따른 바나듐 계열 촉매의 deNOx 특성에 대한 실험을 150~650 °C의 온도영역에서 수행하였고, 이를 수치해석 결과와 비교하였다. Nova 등4) Ciardelli 등5) 그리고 Tronconi 등6)은 바나듐 계열 촉매를 사용하여 Standard- 및 Fast-SCR 반응에 의한 NOx 저감 특성을 실험적으로 분석하였다. 이처럼 바나듐 계열 촉매를 통한 SCR 반응에 대한 다양한 연구가 수행되어왔다.
본 연구에서는 농기계 및 건설기계 등에 사용되는 비 도로용 디젤엔진 질소산화물 저감용 우레아 공급시스템을 개발하기 위한 디젤엔진 SCR 촉매 리그시험장치7)를 구성하였으며, NO/NOx ratio별 촉매 온도 공간속도에 따라 NOx 저감효율을 알아보기 위해 실험을 진행하고 데이터베이스를 구축하였다.
2. 리그시험장치 및 시험 방법
2.1 리그시험장치 구축
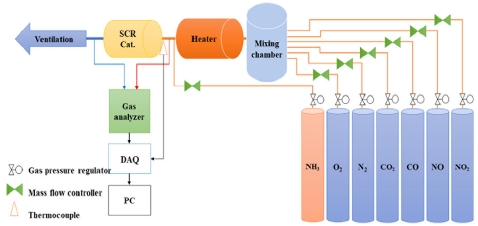
SCR 촉매 성능을 엔진작동과 별도로 평가할 수 있는 실험장치를 구축하였으며 Fig. 1은 SCR 촉매 리그시험장치 개략도를 나타내었으며, Photo. 1은 SCR 촉매 리그시험장 외형이다.
상기 SCR 촉매 리그시험장치는 배기가스 성분을 모사할 수 있는 MFC(Mass flow controller), 배기온도를 모사할 수 있는 Heater, 촉매의 온도를 유지하기 위한 단열박스, 촉매 전/후단의 가스성분을 측정할 수 있는 배기분석기(CLD844CMh), 촉매전단온도를 측정할 수 있는 Thermocouple 및 데이터 취득 및 분석을 위한 DAQ(Data Acquisition) 장치로 구성되었다.
배기가스 성분 모사가스는 N2, O2, CO2, CO, NO, NO2의 혼합가스로 구성되며, 환원제로 기상의 NH3를 공급하였고 각 Bomb에 저장된 가스는 레귤레이터 및 MFC를 통해 목표한 유량으로 제어되어 Mixing chamber를 거쳐 혼합된 후 히터를 통과하며 목표온도에 도달하게 된다.
Heater를 지나 목표온도에 도달한 모사가스에 환원제인 NH3을 공급하게 되고, 촉매 전단과 후단에 Thermocouple 및 배기분석계 통해 모사가스 온도 및 각 가스 농도 측정하였다. 본 실험의 목표 온도는 촉매 전단의 모사가스 온도이다.
모사가스는 SCR 촉매를 통과하면서 NOx 저감반응을 일으키게 되며, 촉매를 통과한 가스의 NOx 및 NH3의 농도를 측정하여 촉매성능특성 파악하였다.
2.2 실험방법 및 조건
SCR촉매의 NOx 저감성능시험의 변수로는 촉매 온도, 공간속도, NO/NOx ratio 며 촉매 온도는 150~550 °C 공간속도는 20,000~120,000h-1로 변환시켰고, NO/NOx ratio 는 100 %, 50 %, 20 %로 시험하였다.
모사가스 조성은 Table 1에 각 모사가스 성분별 함량을 표로 나타내었다.
실험에 사용된 촉매는 Cordierite(근청석) 재질로써 다음 Table 2에 사양을 나타낸 Fresh 촉매와 Aging 촉매며, Aging 조건은 750 °C, 25 hr Hydro-thermal 방식으로 Aging 하였다. 또한 리그 시험용 촉매는 28(x) × 28(y) × 32(z)mm의 사이즈로 가공하여 실험하였으며, Photo. 2는 시험용 촉매의 가공전과 가공후의 외형이다.
3. 실험결과 및 고찰
3.1 촉매전단온도, 공간속도 및 NO/NOx ratio에 따른 NOx 변환효율 측정 및 분석
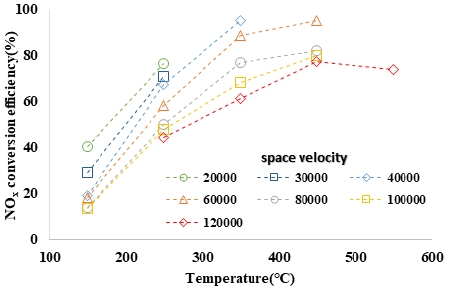
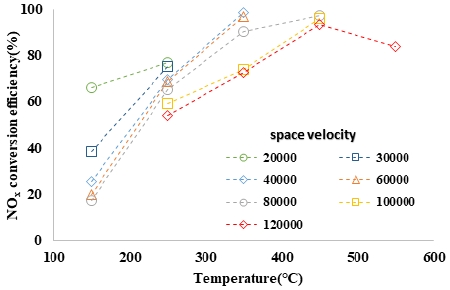
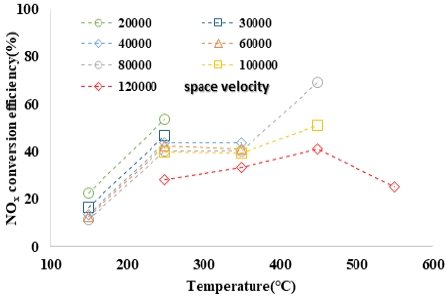
Fig. 2는 NO/NOx ratio가 100 %일 때 촉매전단온도 및 공간속도에 따른 NOx 변환 효율을 나타내었으며, Fig. 3은 NO/NOx ratio가 50 %, Fig. 4는 NO/NOx ratio가 20 %일 때 촉매전단온도 및 공간속도에 따른 NOx의 변환효율을 나타내었다.
SCR 촉매의 NOx 변환효율 측정 결과 350 ~ 450 °C에서 가장 높은 저감효율을 나타내었으며, 500 °C 이상의 고온조건에서는 저감효율이 소폭 감소하는 것을 확인하였다.
촉매 특성 상 기본적으로 온도 상승에 따라 활성화 에너지가 증가하고, 그로 인해 NOx 저감효율이 증가한다.
촉매전단온도 상승에 따라 NH3 산화율이 증가하기 때문에 500 °C 이상의 고온조건에서는 NOx와 반응할 수 있는 NH3의 양이 감소하는 것으로 판단되며, 차후 촉매전단온도에 따른 NH3 산화율을 고려하여 Alpha ratio (NOx/NH3 ratio)를 높임으로써 저감성능을 향상시킬 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
또한 공간속도에 따른 SCR 촉매의 NOx 저감성능 데이터를 살펴보면 공간속도 증가에 따라 저감효율이 감소하는 것을 확인할 수 있으며, 이는 반응에 필요한 시간적 여유가 감소하기 때문으로 판단된다.
NO/NOx ratio에 따른 NOx 저감성능 데이터 분석결과 동일 온도/공간속도 조건에서 기본적으로 NO_50 % 조건에서의 저감성능이 가장 높게 나타났으며, NO/NOx ratio_100 %, NO/NOx ratio_20 % 순의 저감성능을 나타낸다. 이는 standard-SCR 및 fast- SCR 반응에 의한 NOx 저감 특성으로 NO/NOx ratio_100 %와 NO/NOx ratio_20 %보다 NO/NOx ratio_50 %일 때 화학반응이 빠르기 때문으로 판단된다.6)
특히 NO/NOx ratio_50 % 조건에서 250 °C 이하의 저온영역에서의 저감성능이 향상됨을 확인하였다. 또한 NO/NOx ratio_50 % 조건에서는 NO/NOx ratio_100 % 조건과 비교 시 상대적으로 공간속도 증가에 따른 저감성능 저하가 적게 나타났다.
NO/NOx ratio_20 % 조건의 경우 전반적인 저감성능이 낮게 나타나며, 특히 NO/NOx ratio_100 %와 NO/NOx ratio_50 % 조건에서 활발한 반응이 일어나는 350 °C 조건에서도 250 °C 조건과 비교 시 저감효율이 큰 차이를 보이지 않았다.
3.2 SCR 촉매 Aging에 따른 NOx 변환효율 측정 및 분석
Fig. 5는 NO/NOx ratio가 100 %일 때 Fresh 촉매와 Aging 촉매의 온도 및 공간속도에 따른 NOx 변환효율을 나타냈으며, Fig. 6은 NO/NOx ratio_50 %, Fig. 7은 NO/NOx ratio가 20 %일 때 Fresh 촉매와 Aging 촉매의 온도 및 공간속도에 따른 NOx 변환효율을 나타냈었다.
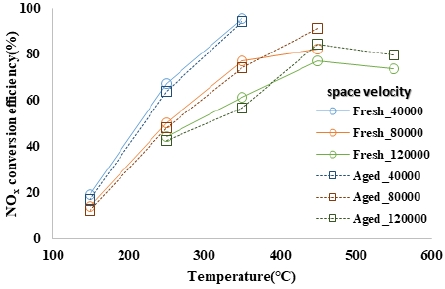
NOx conversion efficiency according to the temperature and space speed of the Fresh and Aging catalysts at NO/NOx ratio_100 %
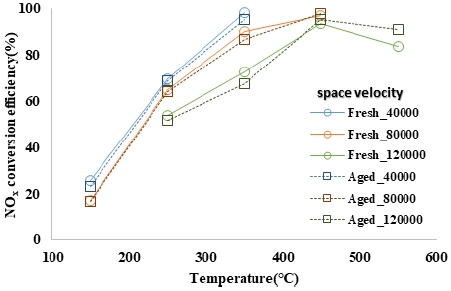
NOx conversion efficiency according to the temperature and space speed of the Fresh and Aging catalysts at NO/NOx ratio_50 %
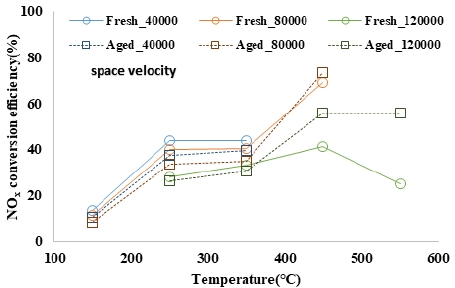
NOx conversion efficiency according to the temperature and space speed of the Fresh and Aging catalysts at NO/NOx ratio_20 %
Aging 촉매의 경우에도 촉매전단온도 및 공간속도에 따른 저감효율의 경향은 Fresh 촉매와 동일하게 나타났으며, 온도 구간별 저감성능을 살펴보면 150 ~ 350 °C 구간에서는 Fresh 촉매의 효율이 높게 나타났으며, 450 °C 이상 구간에서는 Aging 촉매의 효율이 높게 나타났다.
NO/NOx ratio_20 %, 450 °C 이상 조건에서 Fresh 촉매와의 저감효율 차이가 증가하는 것으로 확인하였다.
4. 결 론
본 연구에서는 DCU calibration을 위해 NOx 저감효율 데이터베이스 구축을 위한 디젤엔진 SCR 촉매 리그시험장치를 구성하여 실험을 진행하였으며 다음과 같이 요약할 수 있다.
- 1) SCR 촉매의 NOx 변환효율 측정 결과 온도가 높아질수록 저감효율은 점점 좋아지며 이는 촉매 특성상 기본적으로 온도 상승에 따라 활성화 에너지가 증가되어 NOx 저감효율이 좋아지는 것으로 판단된다.
- 2) 500 °C 이상의 고온에서는 저감효율이 소폭 감소하는데 이는 NH3가 고온에서 산화율이 증가하기 때문에 NOx와 반응 할 수 있는 NH3,의 양이 감소하는 것으로 판단된다.
- 3) Aging 촉매의 경우에도 촉매전단온도 및 공간속도에 따른 저감효율의 경향은 Fresh 촉매와 동일하게 나타나며 NO/NOx ratio가 20 %일 때 450 °C 이상의 구간에서 Fresh촉매와 Aging 촉매의 차이가 증가하는 것으로 나타났다.
Subscripts
| SCR : | selective catalyic reduction |
Acknowledgments
A part of this paper was presented at the KSAE 2019 Spring Conference
이 연구는 2019년도 산업통상자원부 및 산업기술평가관리원(KEIT) 연구비 지원에 의한 연구입니다(과제번호: 10077690).
References
- J. H. Seo, S. W. Lee, Y. S. Cho and Y. S. Kang, “A Study on Effect of NOx and NH3 Emission Characteristics by Urea-SCR Model for Euro-6 Emission Regulation in Diesel Engine,” KSAE Annual Conference Proceedings, pp.479-485, 2012.
-
R. M. Heck, “Catalytic Abatement of Nitrogen Oxides-stationary Applications,” Catalysis Today, Vol.53, No.4, pp.519-523, 1999.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-5861(99)00139-X]
-
C. Winkler, P. Florchinger, M. D. Patil, J. Gieshoff, P. Spurk and M. Pfeifer, “Modeling of SCR DeNOx Catalyst-looking at the Impact of Substrate Attributes,” SAE 2003-01-0845, 2003.
[https://doi.org/10.4271/2003-01-0845]
-
I. Nova, C. Ciardelli, E. Tronconi, D. Chatterjee and B. B. -Konrad, “NH3-NO/NO2 Chemistry over V-based Catalysts and Its Role in the Mechanism of the Fast-SCR Reaction,” Catalysis Today, Vol.114, No.1, pp.3-12, 2006.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2006.02.012]
-
C. Ciardelli, I. Nova, E. Troconi, D. Chatterjee, B. B.-Konrad, M. Weibel and B. Krutzsch, “Reactivity of NO/NO2-NH3 SCR System for Diesel Exhaust Aftertreatment: Identification of the Reaction Network as a Function of Temperaure and NO2 Feed Content,” Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, Vol.70, Nos.1-4, pp.80-90, 2007.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2005.10.041]
-
E. Tronconi, I. Nova, C. Ciardelli, D. Chatterjee and M. Weibel, “Redox Features in the Catalytic Mechanism of the ‘Standard’ and ‘Fast’ NH3-SCR of NOx over a V-based Catalyst Investigated by Dynamic Methods,” Journal of Catalysis, Vol.245, No.1, pp.1-10, 2007.
[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2006.09.012]
- J. D. Kim and S. H. Kang, “A Study on NOx and NH3 Emission Characteristics for Database Construction of NOx Reduction Performance and NH3 Adsorption・Desorption Characteristics of SCR Catalyst,” KSAE Spring Conference Proceedings, p.270, 2019.